Discover more about how the Spotify Model transforms education.
The Spotify Model originated as a framework for agile teamwork in the tech industry, developed by Spotify to maintain efficiency and innovation at scale. However, its principles extend far beyond software development.
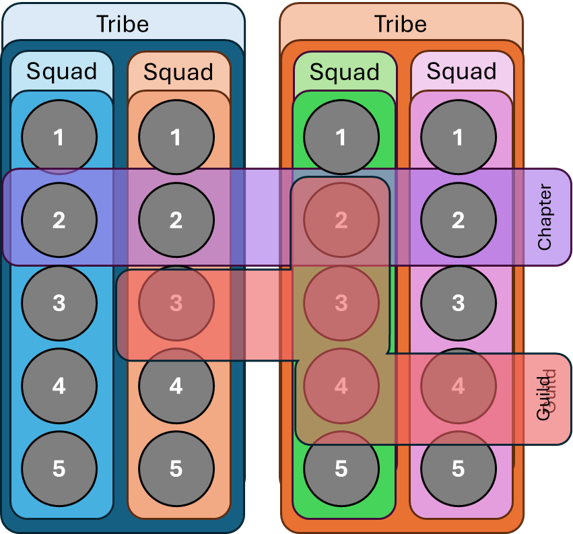
In education, the Spotify Model restructures classrooms to mirror real-world teamwork. It replaces rigid, top-down instruction with a dynamic, student-driven approach. By dividing learners into interconnected units—Squads, Tribes, Chapters, and Guilds—it promotes autonomy, collaboration, and mastery.
This model fosters a balance between structure and flexibility, ensuring students not only meet curriculum objectives but also develop real-world problem-solving and teamwork skills.
A Squad is a small, self-organizing student group working towards a common goal. Each Squad is autonomous, meaning they decide how to collaborate, allocate tasks, and tackle challenges.
Squads ensure every student has an active role in learning. By taking ownership of their projects, students build confidence, problem-solving skills, and accountability.
In a History lesson about World War II, Squads might focus on different perspectives:
Each Squad synthesizes their findings and presents them, ensuring a comprehensive, student-led exploration of the topic.
A Tribe is a collection of Squads working towards related objectives. This structure encourages cross-team collaboration, breaking down learning silos and fostering shared knowledge.
Tribes allow students to see the bigger picture while maintaining individual Squad autonomy.
In a Science lesson on Newton’s Laws of Motion:
Together, they form a Motion & Forces Tribe, collaborating to connect findings and deepen understanding.
A Chapter is a specialized learning group focused on skill development rather than content. While Squads work towards project goals, Chapters ensure consistent expertise across multiple Squads.
Chapters allow students to refine their technical and analytical skills in a focused environment.
In a Computing class working on a software project:
A Coding Standards Chapter might form, ensuring best practices are followed across all Squads.
A Guild is an interest-based community that extends beyond the curriculum. Unlike Chapters (which focus on skills), Guilds allow students to explore their passions in a collaborative environment.
Guilds encourage self-driven learning and innovation, helping students connect their studies with real-world applications.
In a Cybersecurity course, students passionate about ethical hacking might form a Cybersecurity Guild, organizing competitions and workshops beyond the regular syllabus.
Please note that all resources are free to download and distribute.